Setting up OPTEE and Linux for the Pine A64
The Pine A64 is a board running the A64 SoC and comes in three different variants:
- Pine A64 512MB
- Pine A64+ 1GB
- Pine A64+ 2GB (this is the one I have)
Allwinner is the manufacturer of the A64 SoC which is a Quad-core Cortex-A53 ARM CPU and a Mali400 MP2 GPU from ARM. The Cortex A53 implements the AArch64 architecture.
Although Allwinner provides a BSP(Board-Support-Package), the U-Boot bootloader doesn’t compile and the Linux kernel image is patched (and outdated) so it’s better to compile mainline kernel and U-Boot as support for Pine A64 is present.
Boot Flow
OP-TEE can be booted on the Pine A64 in combination with Linux. In this setup, the boot flow is as follows:
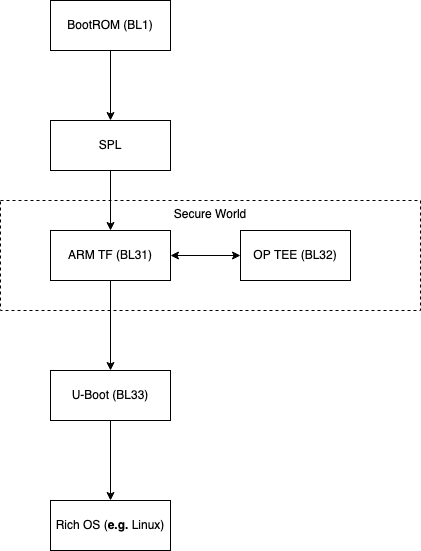
The BootROM code, considered BL1, is loaded from the chips ROM which in turn loads the SPL responsible for initializing DRAM and loading OP-TEE, ARM-TF and U-Boot to memory. The processor then branches to ARM-TF which first loads OP-TEE and then hands control over to U-Boot, the normal world bootloader, which will load the normal world kernel.
Firmware
The Pine A64 firmware is made up of four different parts:
- The on-chip Boot-ROM (BROM), which is the first code to be executed and cannot be modified
- A Secondary Program Loader (SPL) responsible for initializing DRAM and loading the remaining firmware parts. This component is part of U-Boot
- EL3 runtime firmware (i.e ARM TF-A), support for A64 SoC is present in mainline
- U-Boot bootloader for loading kernels and data; support for A64 is present in upstream
Build
This document takes all the components from mainline/upstream, instead of the ones provided by Sunxi.
Tooling
To build the different components (ARM TF-A, U-Boot, Linux), setup a cross compilation toolchain and add the binaries to the PATH env variable:
export PATH=$PATH:<path to aarch64 binaries>:<path to aarch32 binaries>
export CROSS_COMPILE="ccache aarch64-linux-gnu-"
- U-Boot requires
swig,python-devanddevice-tree-compilerpackages to be present on the system. - Linux kernel modules require
kmodto be installed.
ARM TF-A
ARM Trusted Firmware is responsible for the EL3 runtime secure monitor in the Pine A64, switching between the secure and normal world, S-EL1 and EL1. The following sequence of commands is enough to compile it for the Pine A64:
git clone https://review.trustedfirmware.org/TF-A/trusted-firmware-a
cd trusted-firmware-a
git checkout <latest stable release> (e.g. v2.2)
make PLAT=sun50i_a64 SPD=opteed DEBUG=1 bl31
export BL31=$(pwd)/build/sun50i_a64/debug/bl31.bin
OPTEE
OP-TEE is made up of two essential components, the (secure) OS itself, OPTEE OS, and a client which will run in the normal world and interact with OPTEE OS via the OPTEE driver provided by the (Linux) kernel.
OPTEE OS
git clone https://github.com/OP-TEE/optee_os.git -b <latest stable release> (e.g. 3.8.0)
cd optee_os
make CFG_ARM64_CORE=y \
CFG_TEE_LOGLEVEL=4 \
CFG_TEE_CORE_LOG_LEVEL=4 \
CROSS_COMPILE32="ccache arm-linux-gnueabihf-" \
CROSS_COMPILE64="ccache aarch64-linux-gnu-" \
DEBUG=1 \
PLATFORM=sunxi-sun50i_a64
export TEE=$(pwd)/out/arm-plat-sunxi/core/tee-pager_v2.bin
The file pointed to by TEE is a RAW ARM executable which will be branched to by ARM TF-A.
OPTEE Client
git clone https://github.com/OP-TEE/optee_client -b <latest stable release> (e.g. 3.8.0)
cd optee_client
make
cd out/export
tar -cfv optee_client.tar.gz usr
The resutling tar archive should be placed in the root partition in the respective subdirectories.
U-Boot
U-Boot is the normal world bootloader, however the repo also includes a SPL which will be loaded by BL1.
Modifications
The binary image built for the Pine A64+ board in mainline U-Boot doesn’t load OPTEE, thus the
script used to generate the Device Tree Binary must be patched. The patched version
should be copied to board/sunxi/mksunxi_fit_atf.sh
git clone https://gitlab.denx.de/u-boot/u-boot.git
cd u-boot
git checkout <latest stable release> (e.g. v2020.04-rc3)
make pine64_plus_defconfig
make
export PATH=$PATH:$(pwd)/tools/
The SPL, U-Boot plus TF-A and OP-TEE are packaged in u-boot-sunxi-with-spl.bin which will later be flashed
before the first partition of the SD Card at an 8Kb offset:
dd if=u-boot-sunxi-with-spl.bin of=/dev/sdx bs=1k seek=8
Linux
Modifications
The mainline kernel provides enought support for a headless setup of the Pine A64 (e.g.: serial + ssh), however in order for the HDMI output to work and the OP-TEE driver to be loaded at boot, some modifications must be introduced.
- The default kernel configuration for the Pine A64+ board doesn’t enable the Mali400 GPU driver, so it
must be enabled manually via the menuconfig target when running
make menuconfig, after step 3. - Modify the DTS (Device Tree Source) file in
arch/arm64/boot/dts/allwinner/sun50i-a64-pine64-plus.dtsto include the following block:firmware { optee { compatible = "linaro,optee-tz"; method = "smc"; }; };which enables the kernel to identify and load the OP-TEE at boot time.
Steps
- Clone the mainline repo, latest version
git clone https://github.com/torvalds/linux.git -b v5.6 --depth=1 cd linux -
Replace the DT source for the Pine A64, in
arch/arm64/boot/dtswith the new one -
Generate a configuration:
make ARCH=arm64 defconfig -
Create the kernel image:
make ARCH=arm64 -j2 Imagewhich is placed inarch/arm64/boot/ -
Compile the device tree for the Pine A64:
make ARCH=arm64 -j2 dtbs; the dtb file will be placed inarch/arm64/boot/dts/ - Compile the kernel modules which include the Mali 400 GPU driver needed for HDMI output:
make -j2 ARCH=arm64 modules make -j2 ARCH=arm64 INSTALL_MOD_PATH=modules modules modules_install - Create a tar archive with the kernel modules
tar -czf modules.tar.gz modules
Partitioning the SD Card
Partitioning the SD card can be achievied by running the following sequence of commands:
sudo dd if=/dev/zero of=/dev/sdX bs=1M count=1
blockdev -rereadpt /dev/sdX
cat <<EOT | sfdisk /dev/sdX
2M,32M,c
,,L
EOT
mkfs.vfat /dev/sdX1
mkfs.ext4 /dev/sdX2
U-Boot Configuration
U-Boot is configured via a file, boot.cmd, which will be wrapped by a U-boot header. To configure U-Boot:
- Mount the boot partition
/dev/sdX1in/mntand create theboot.cmdfile as such:
fatload mmc 0 0x46000000 Image
fatload mmc 0 0x49000000 sun50i-a64-pine64-plus.dtb
setenv bootargs console=ttyS0,115200 console=tty1 earlyprintk root=/dev/mmcblk0p2 rootwait panic=10
booti 0x46000000 - 0x49000000
- Copy the kernel
Imageand the device tree<board>.dtbto the boot partition and run:mkimage -C none -A arm64 -T script -d boot.cmd boot.scr
Rootfs
There are several utilities to create a root filesystem, deboostrap is one such tool. Mount the root
partition /dev/sdX2 in /mnt:
- Use
debootstrapto install a Debian base system on the root partition - Chroot into the mounted partition, using qemu:
chroot /mnt /usr/bin/qemu-aarch64-static /bin/sh -i - Run
/deboostrap/deboostrap --second-stage
Kernel Modules
With the boot partition mounted on /mnt:
- Extract the modules from the tar archive
tar -xf modules.tar.gz - Copy the modules to the root filesystem
cp -r modules/lib/ /mnt/lib